Regional scientific and medical conferences
We are actively participating in all regional scientific and medical conferences to make sure our technological achievements are well known and new research is always following latest scientific trends

Personal collaboration
The most important part in any research is people. We invest in our scientists qualifications and make sure that they get all the latest news, trends, they participate in various collaborations and research. That's why we are among the top laboratories regarding quality and innovations
The high human and economic costs associated with medical cases make it more important than ever to rapidly accelerate and scale medical innovations.
is made up by many dedicated individuals that work together as a team to help facilitate the healthcare innovation process. We are passionate about cutting-edge healthcare technologies with a focus on those that will have the greatest societal impact and meaningfully improve patient care.
Clinical trials and related projects
To ensure quality and efficiency of medical products we are continuously performing clinical trials with various groups of patients, we are also collaborating with other laboratories working in the same area of research to share knowledge and experience.
Process is important
The process of clinical trials is important and has to follow all regulations from governmental institutions. All research is done in four big phases and only then new products are safe and ready to use for all patients worldwide.
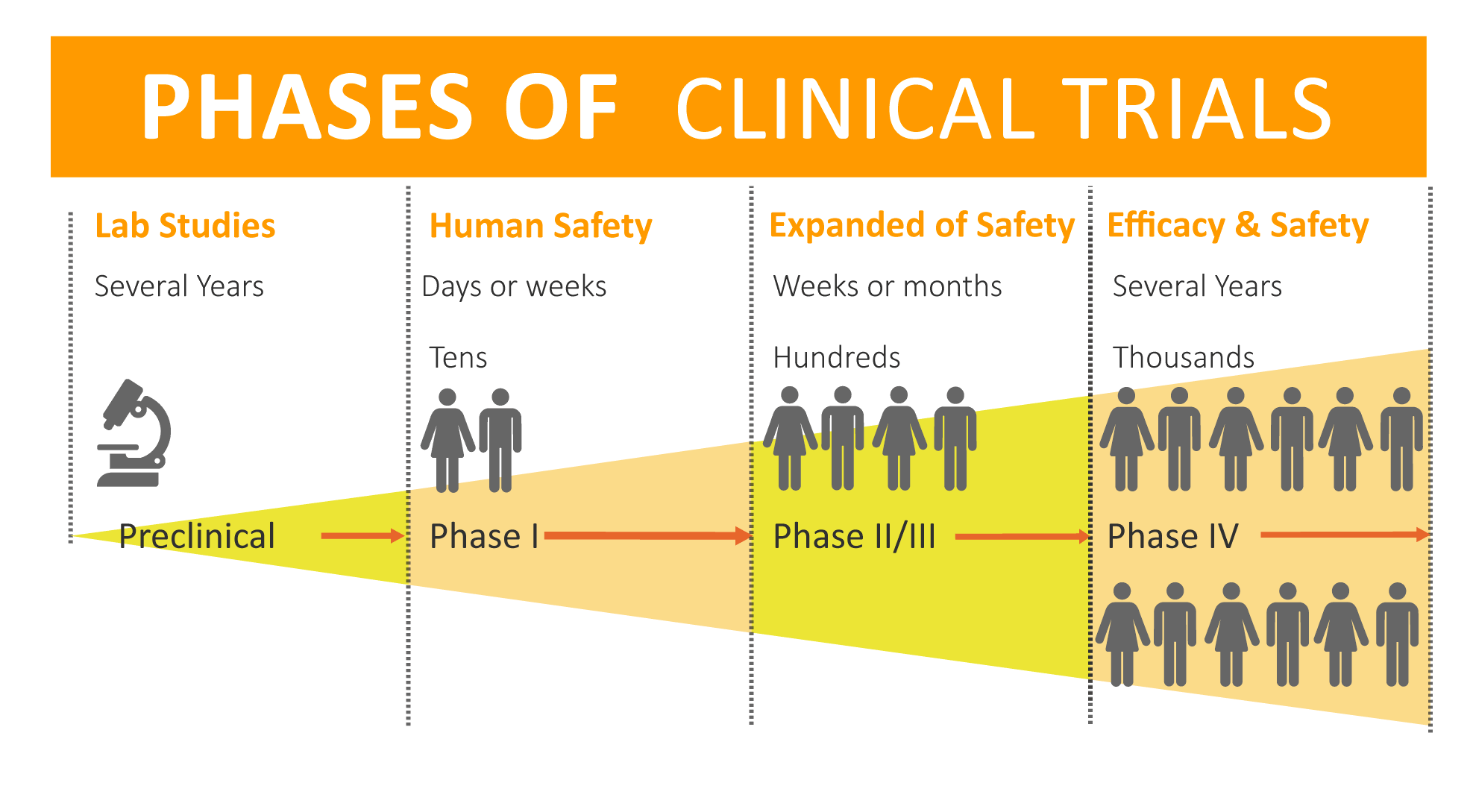
Clinical trials advance through four phases to test a treatment, find the appropriate dosage, and look for side effects. If, after the first three phases, researchers find a drug or other intervention to be safe and effective, the FDA approves it for clinical use and continues to monitor its effects.
Clinical trials of drugs are usually described based on their phase. The FDA typically requires Phase I, II, and III trials to be conducted to determine if the drug can be approved for use.
- A Phase I trial tests an experimental treatment on a small group of often healthy people (20 to 80) to judge its safety and side effects and to find the correct drug dosage.
- A Phase II trial uses more people (100 to 300). While the emphasis in Phase I is on safety, the emphasis in Phase II is on effectiveness. This phase aims to obtain preliminary data on whether the drug works in people who have a certain disease or condition. These trials also continue to study safety, including short-term side effects. This phase can last several years.
- A Phase III trial gathers more information about safety and effectiveness, studying different populations and different dosages, using the drug in combination with other drugs. The number of subjects usually ranges from several hundred to about 3,000 people. If the FDA agrees that the trial results are positive, it will approve the experimental drug or device.
- A Phase IV trial for drugs or devices takes place after the FDA approves their use. A device or drug's effectiveness and safety are monitored in large, diverse populations. Sometimes, the side effects of a drug may not become clear until more people have taken it over a longer period of time.
Collaboration with universities
As part of our Academic Relations Programme researchers can collaborate with experts from multiple disciplines, such as dentistry, nursing, pharmacy, public health, and veterinary medicine. Such collaboration enables our doctors to turn discoveries into preventions, treatments, and cures for diseases such as cancer and diabetes more quickly and efficiently.

Working together
Research at the Medical School's departments, centers, and institutes extends from basic science, that increases our scientific knowledge base, to clinical and translational research, where scientific discoveries are moved from the laboratory to real-world practice.
As industry gains insight through the program, the students build their research chops and real-world experience. The collaborative program provides students with the opportunity to shape the development of medical tech innovations with large companies.
Industry partnerships give students and faculty additional funding. By striking up corporate partnerships, universities have more resources to undertake research, and they’re able to diversify their research areas.
But—it’s not all about the money. If you break up the university benefits into a pie chart, one big slice would be industry feedback and guidance. Universities know that some problems can’t be solved in isolation in a lab, and industry feedback is key to taking an invention or product from conception to market.

